 Framework
FrameworkAbstract
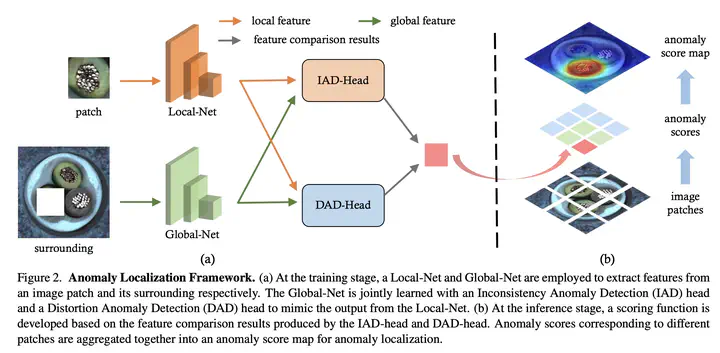
Anomaly localization, with the purpose to segment the anomalous regions within images, is challenging due to the large variety of anomaly types. Existing methods typically train deep models by treating the entire image as a whole yet put little effort into learning the local distribution, which is vital for this pixel-precise task. In this work, we propose an unsupervised patch-based approach that gives due consideration to both the global and local information. More concretely, we employ a Local-Net and Global-Net to extract features from any individual patch and its surrounding respectively. Global-Net is trained with the purpose to mimic the local feature such that we can easily detect an abnormal patch when its feature mismatches that from the context. We further introduce an Inconsistency Anomaly Detection (IAD) head and a Distortion Anomaly Detection (DAD) head to sufficiently spot the discrepancy between global and local features. A scoring function derived from the multi-head design facilitates high-precision anomaly localization. Extensive experiments on a couple of real-world datasets suggest that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art competitors by a sufficiently large margin.